
If one has a 3 σ event (properly, a 3 s event) and substantially fewer than 300 samples, or a 4 s event and substantially fewer than 15,000 samples, then a normal distribution will understate the maximum magnitude of deviations in the sample data. (number of sample standard deviations that a sample is above or below the sample mean), and compares it to the 68–95–99.7 rule: Simple back-of-the-envelope test takes the sample maximum and minimum and computes their z-score, or more properly t-statistic These plots are easy to interpret and also have the benefit that outliers are easily identified. For normal data the points plotted in the QQ plot should fall approximately on a straight line, indicating high positive correlation. Here the correlation between the sample data and normal quantiles (a measure of the goodness of fit) measures how well the data are modeled by a normal distribution. Lack of fit to the regression line suggests a departure from normality (see Anderson Darling coefficient and minitab).Ī graphical tool for assessing normality is the normal probability plot, a quantile-quantile plot (QQ plot) of the standardized data against the standard normal distribution. In this case one might proceed by regressing the data against the quantiles of a normal distribution with the same mean and variance as the sample. This might be difficult to see if the sample is small. The empirical distribution of the data (the histogram) should be bell-shaped and resemble the normal distribution. A number of statistical tests, such as the Student's t-test and the one-way and two-way ANOVA require a normally distributed sample populationĪn informal approach to testing normality is to compare a histogram of the sample data to a normal probability curve. In Bayesian statistics, one does not "test normality" per se, but rather computes the likelihood that the data come from a normal distribution with given parameters μ, σ (for all μ, σ), and compares that with the likelihood that the data come from other distributions under consideration, most simply using a Bayes factor (giving the relative likelihood of seeing the data given different models), or more finely taking a prior distribution on possible models and parameters and computing a posterior distribution given the computed likelihoods.Ī normality test is used to determine whether sample data has been drawn from a normally distributed population (within some tolerance).In frequentist statistics statistical hypothesis testing, data are tested against the null hypothesis that it is normally distributed.In descriptive statistics terms, one measures a goodness of fit of a normal model to the data – if the fit is poor then the data are not well modeled in that respect by a normal distribution, without making a judgment on any underlying variable.

More precisely, the tests are a form of model selection, and can be interpreted several ways, depending on one's interpretations of probability:
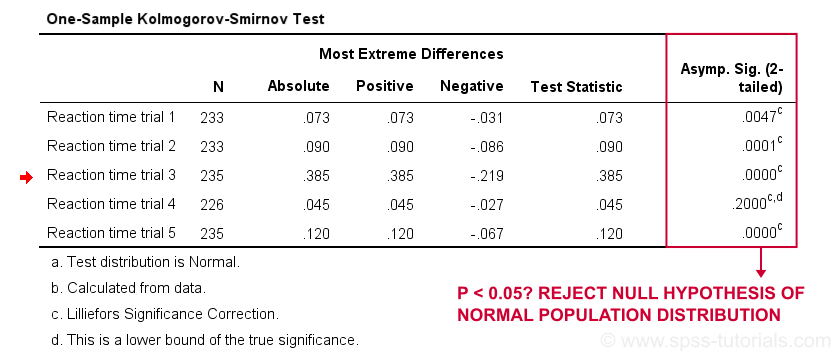

In statistics, normality tests are used to determine if a data set is well-modeled by a normal distribution and to compute how likely it is for a random variable underlying the data set to be normally distributed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
